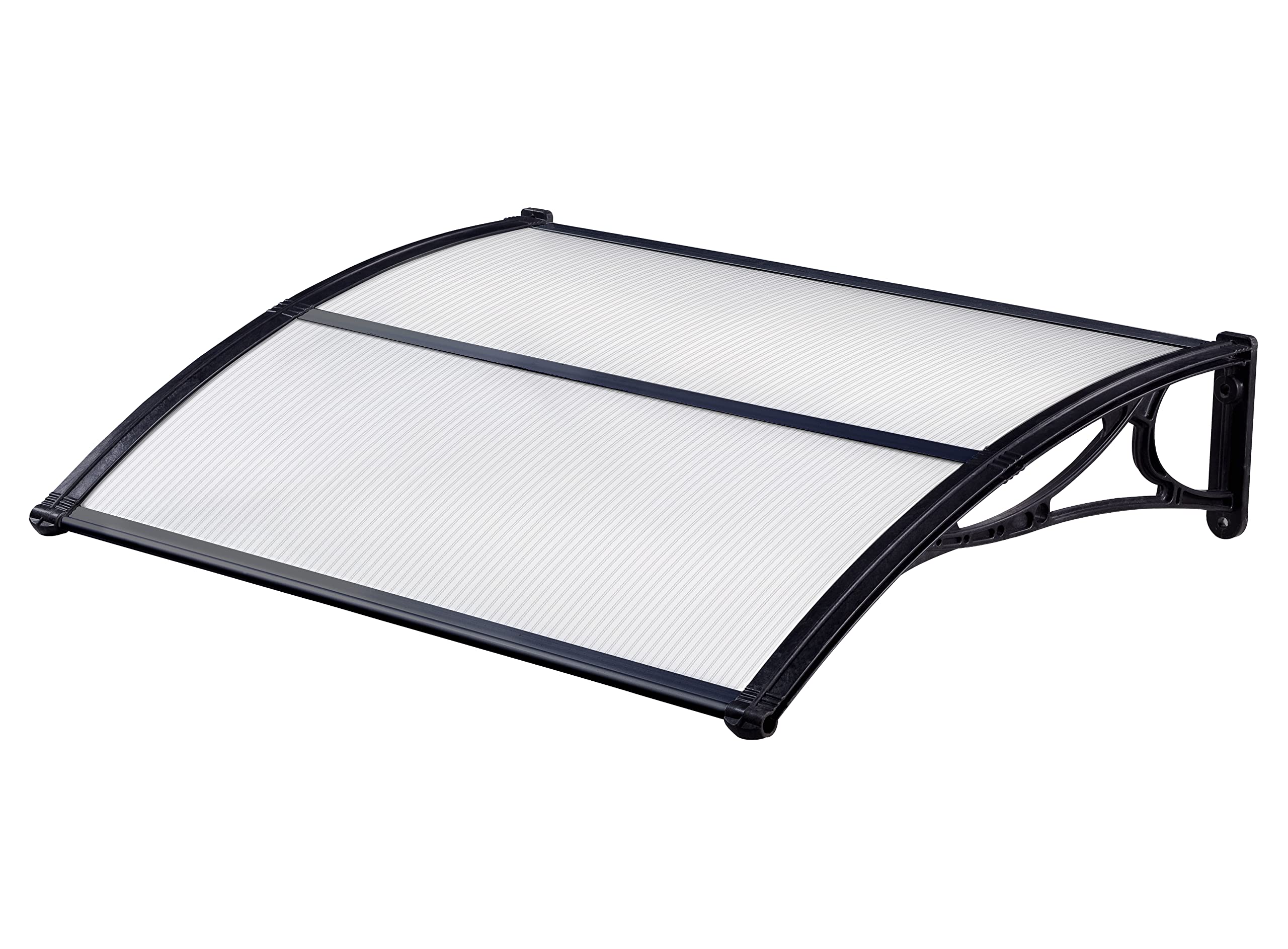
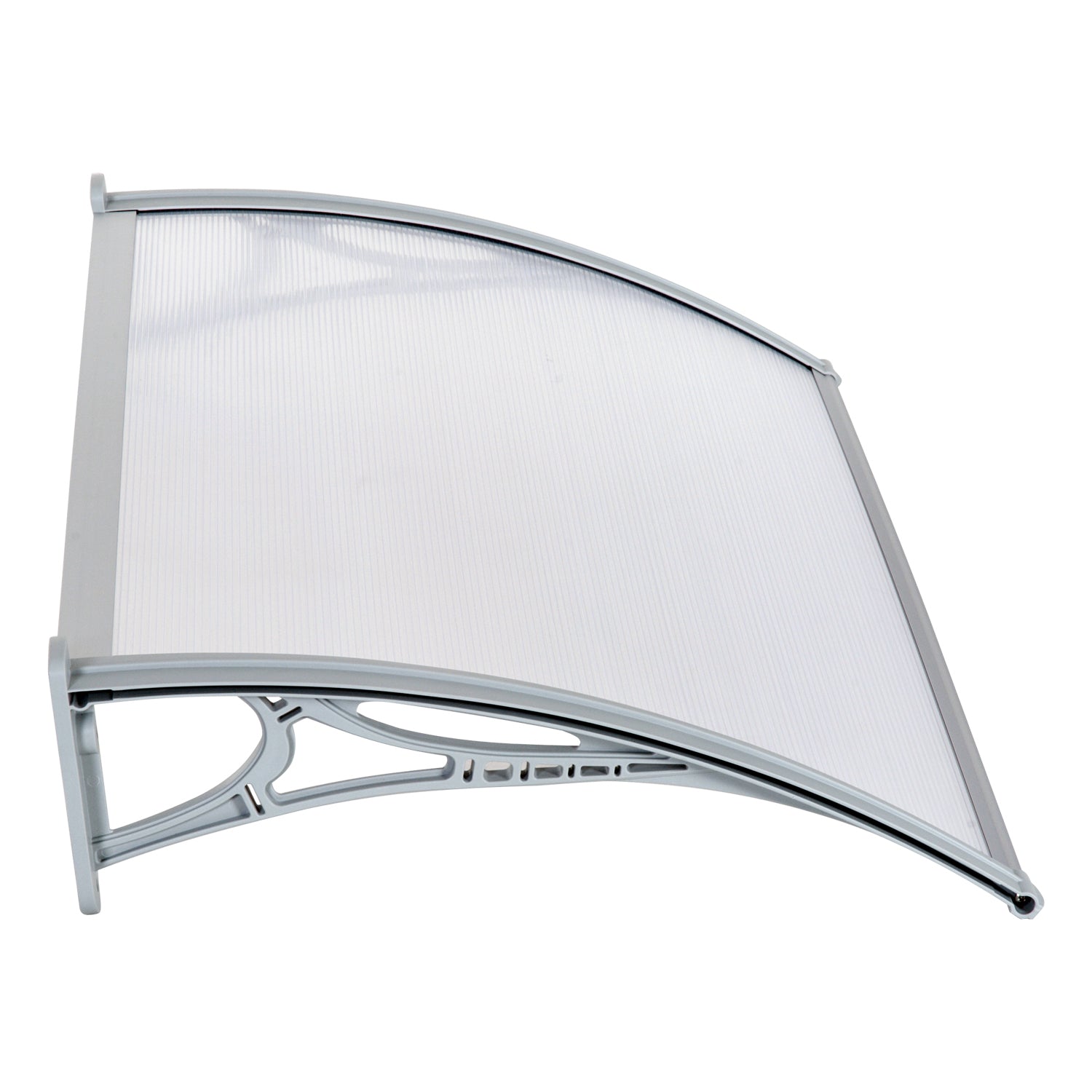
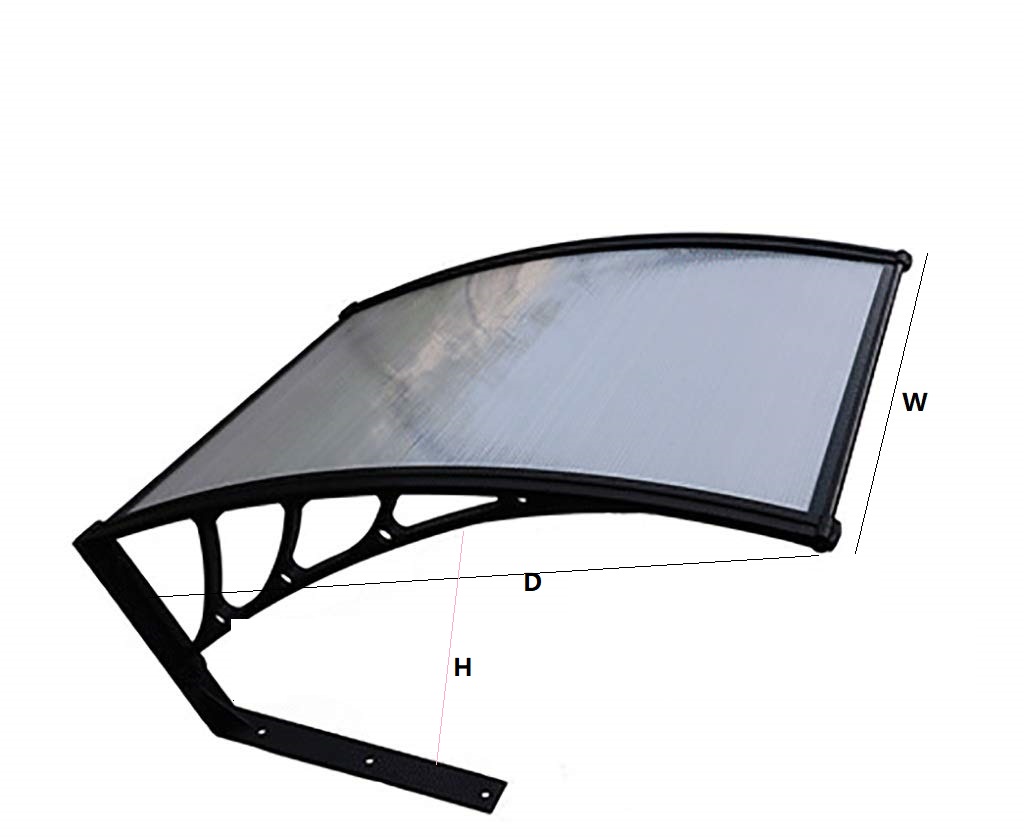
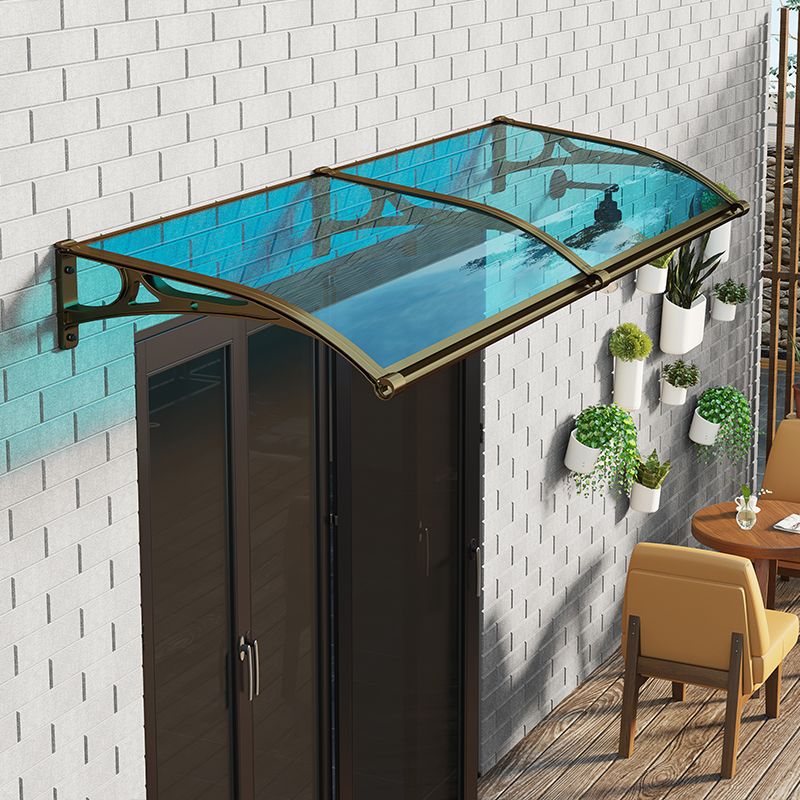
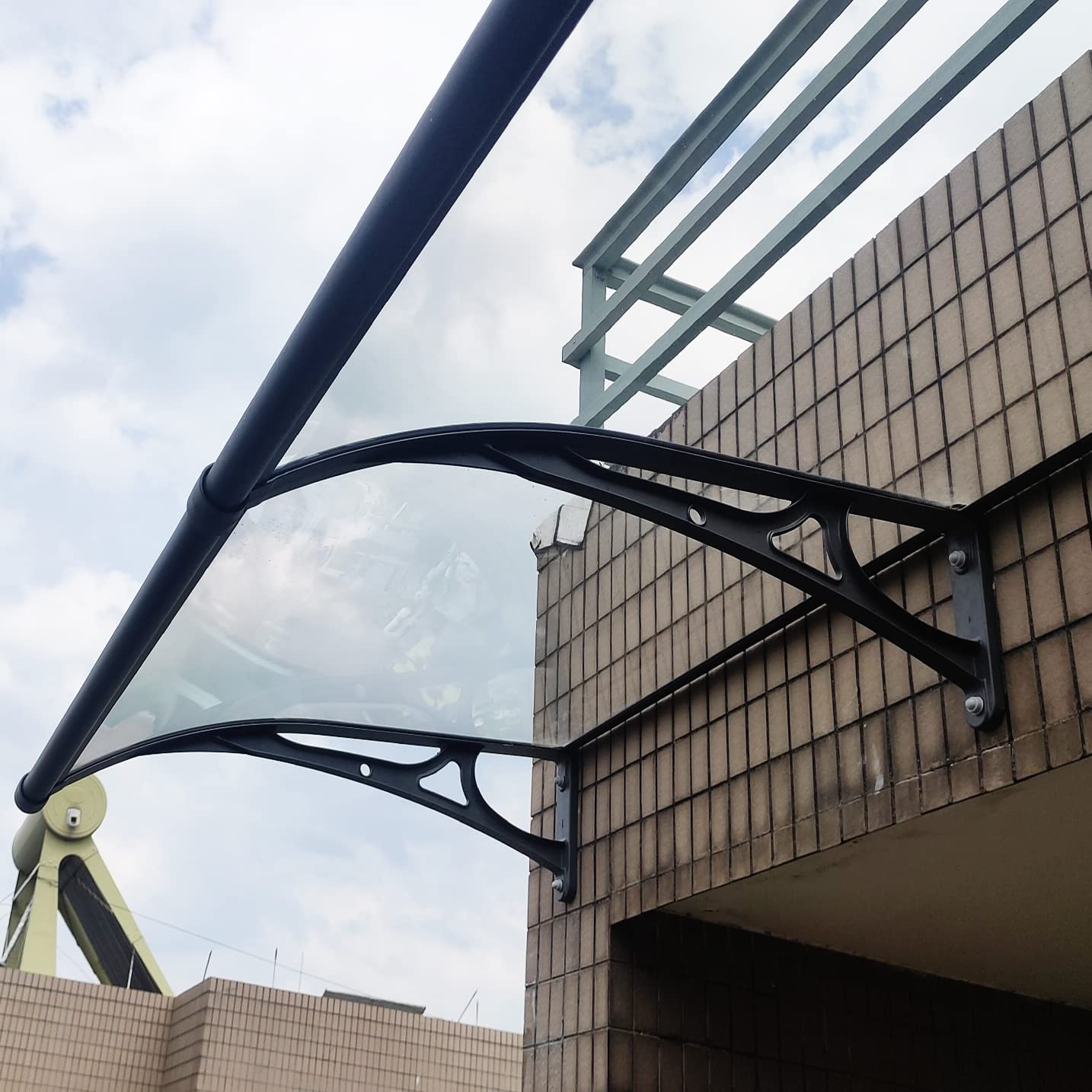
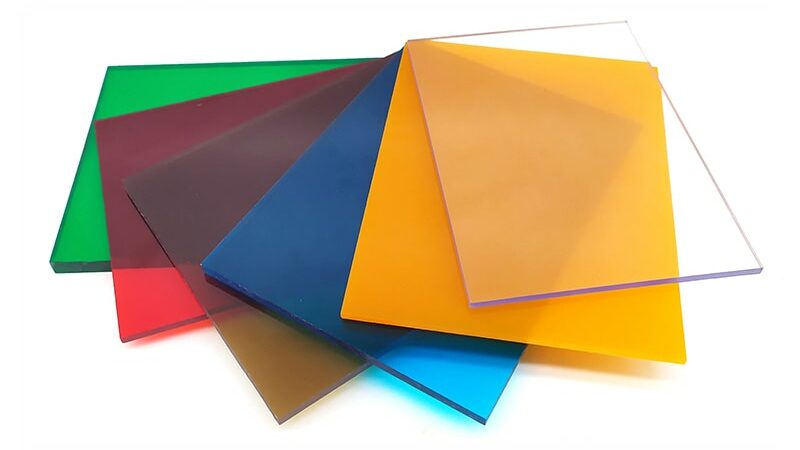
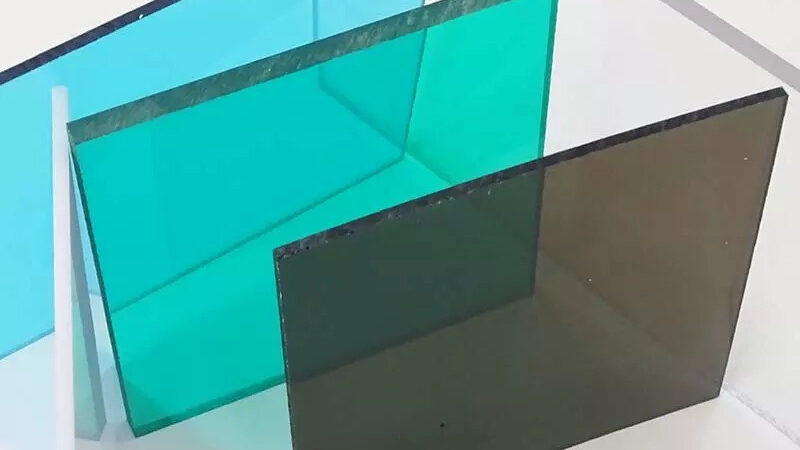
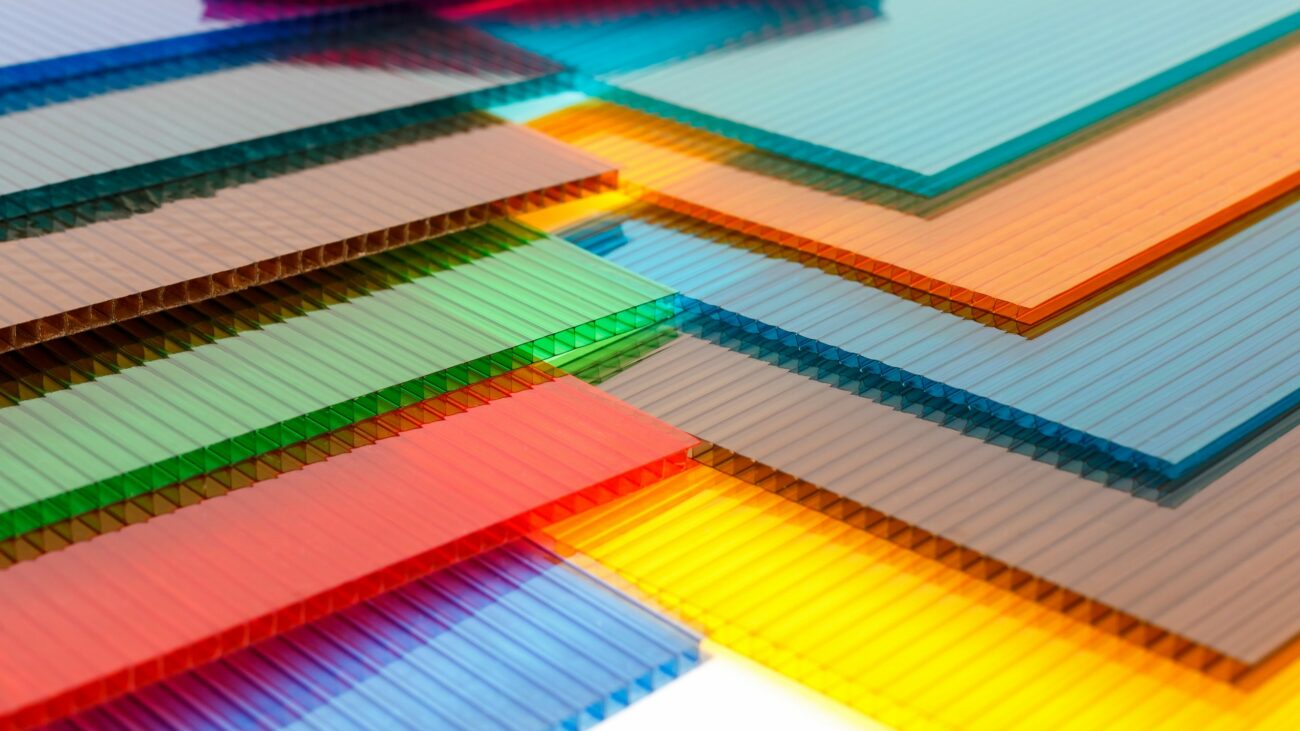
What is polycarbonate sheet?
Polycarbonate sheet (PC) is a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in chemical structure. The polycarbonate sheet used in the project is a strong and tough material, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easy to process, form and heat form. Because of these characteristics, polycarbonate has found many applications. Polycarbonate has no resin identification code (RIC) of xxx and is identified as “other” in the RIC list, 7. Products made from polycarbonate may contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA).

Properties and processing editing of polycarbonate
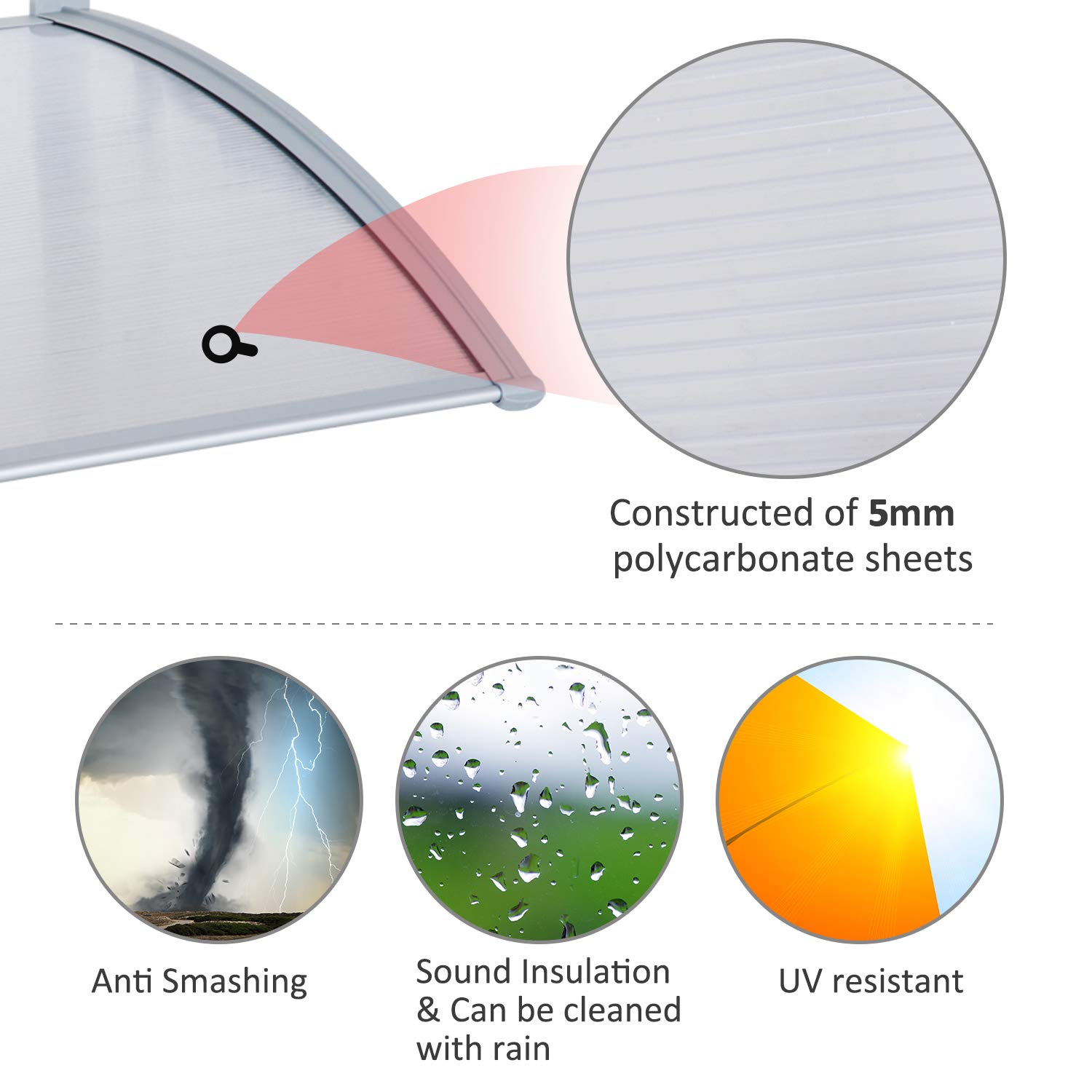
Polycarbonate is a durable material. Although it has high impact resistance, its scratch resistance is very low. Therefore, the hard coating is applied to polycarbonate glasses and polycarbonate external automotive components. Compared with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA, acrylic acid), polycarbonate has stronger properties and longer retention time at extreme temperatures. Heat treatment materials are usually completely amorphous, so they are highly transparent to visible light and have better light transmittance than many kinds of glass.
The glass transition temperature of polycarbonate is about 147 ° C (297 ° F), so it gradually softens above this temperature and flows above about 155 ° C (311 ° F). The tool must be kept at high temperature, usually higher than 80 ° C (176 ° F), to produce strain-free and stress-free products. The low molecular weight grade is easier to form than the high grade, but its strength is therefore lower. The toughest brand has the highest molecular weight, but it is more difficult to process.
Unlike most thermoplastics, polycarbonate can withstand large plastic deformation without cracking or fracture. Therefore, it can be processed and formed using sheet metal technology at room temperature, such as bending on the brake. Even for sharp bends with small radii, heating may not be necessary. This makes it valuable in prototype design applications that require transparent or non-conductive parts, which cannot be made of metal plates. PMMA/acrylic, similar in appearance to polycarbonate, fragile, and cannot be bent at normal temperature.
Main conversion technologies of polycarbonate resin:
- Extruded into tubes, bars and other profiles, including multi-wall
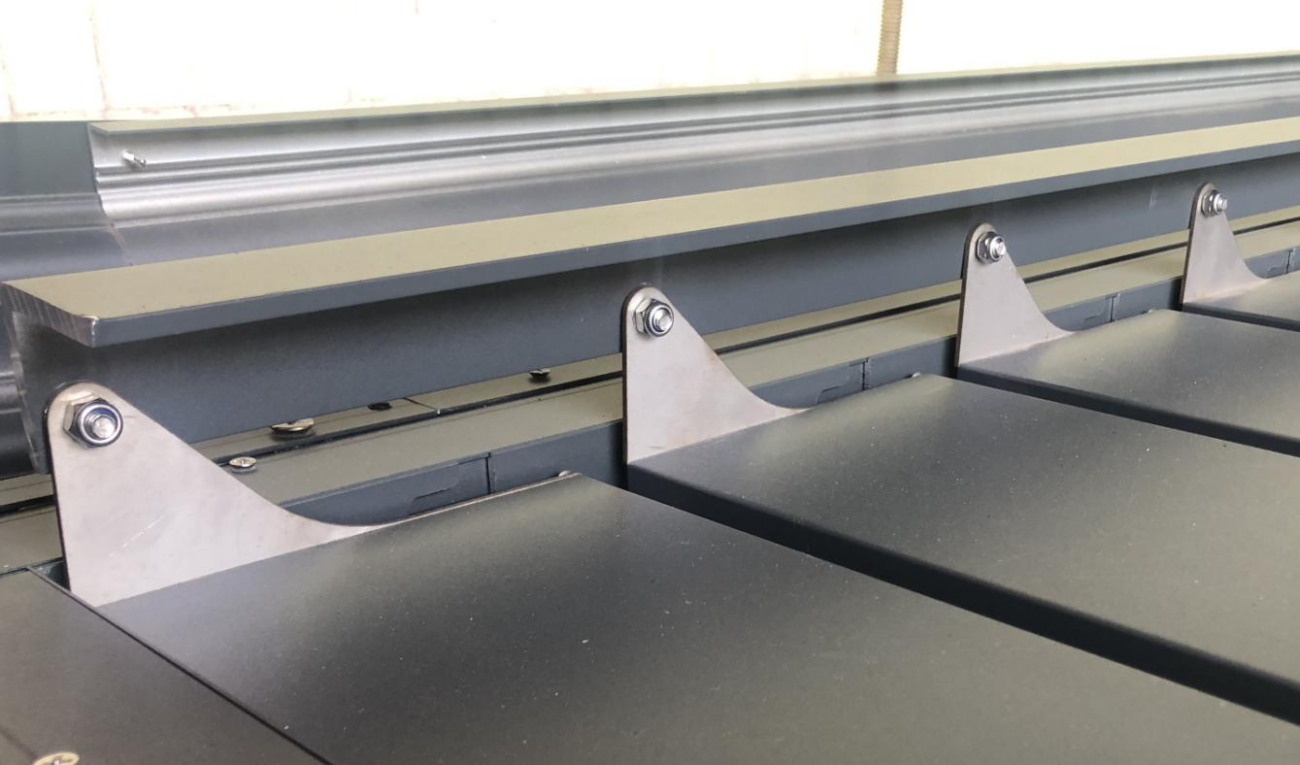
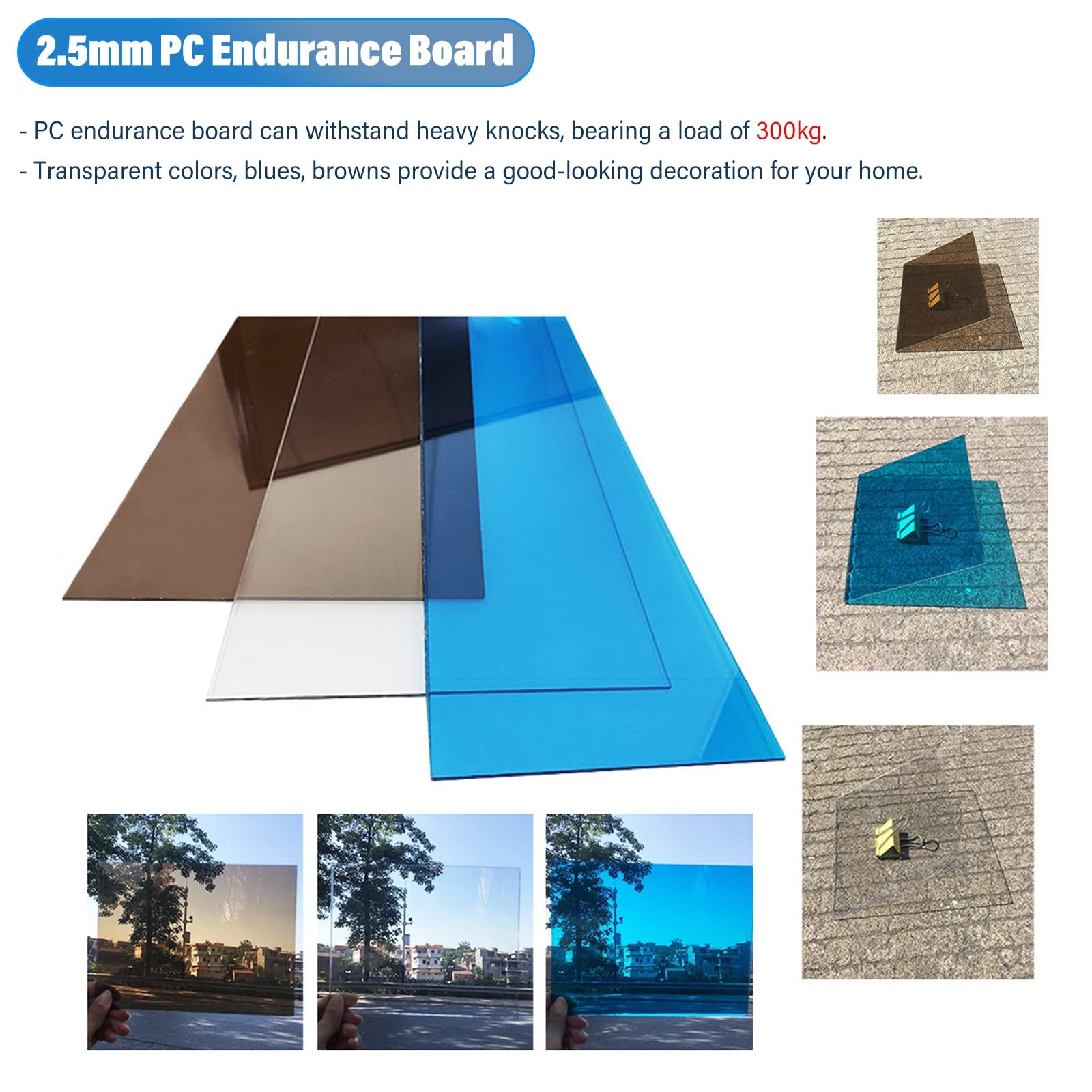
- Extruded into sheet (0.5-20 mm (0.020-0.787 in)) and film (less than 1 mm (0.039 in)) by cylinder (calender), which can be directly manufactured into other shapes, such as bending, drilling or wiring, using thermal forming or secondary manufacturing technology. Because of its chemical properties, it is not conducive to laser cutting.
- Injection molding into finished products
Polycarbonate may become brittle when exposed to ionizing radiation of more than 25kGy (J/kg).
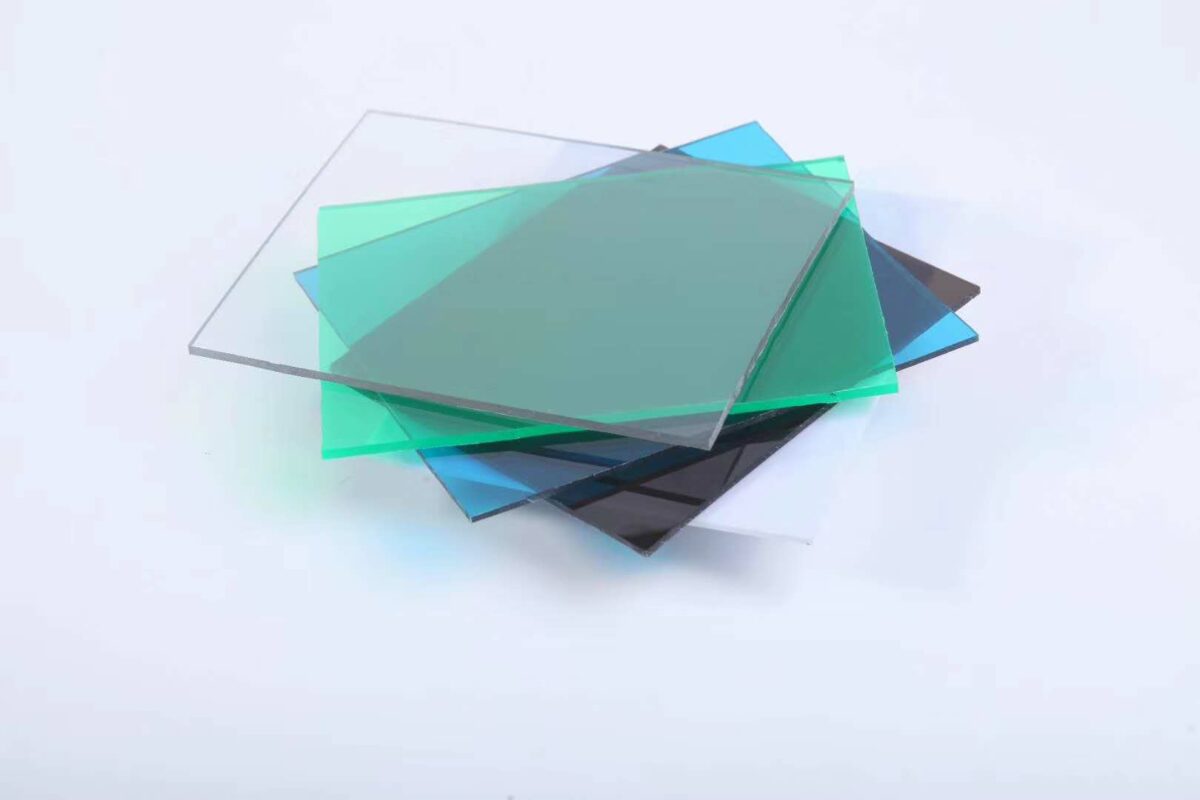

Polycarbonate sheet https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Amas-clear-greenhouse-panels-waterproof-solid_1600294223529.html?spm=a2700.shop_plgr.41413.2.4a336923TgS0sS
Application of polycarbonate sheet
Electronic component
Polycarbonate is mainly used for electronic applications that utilize its collective safety characteristics. As a good electrical insulator with heat resistance and flame retardance, it is used in various products related to electrical and telecommunication hardware. It can also be used as a dielectric in high stability capacitors. However, after Bayer, the manufacturer of xxx, stopped producing condenser grade polycarbonate film at the end of 2000, the commercial production of polycarbonate capacitors mostly stopped.
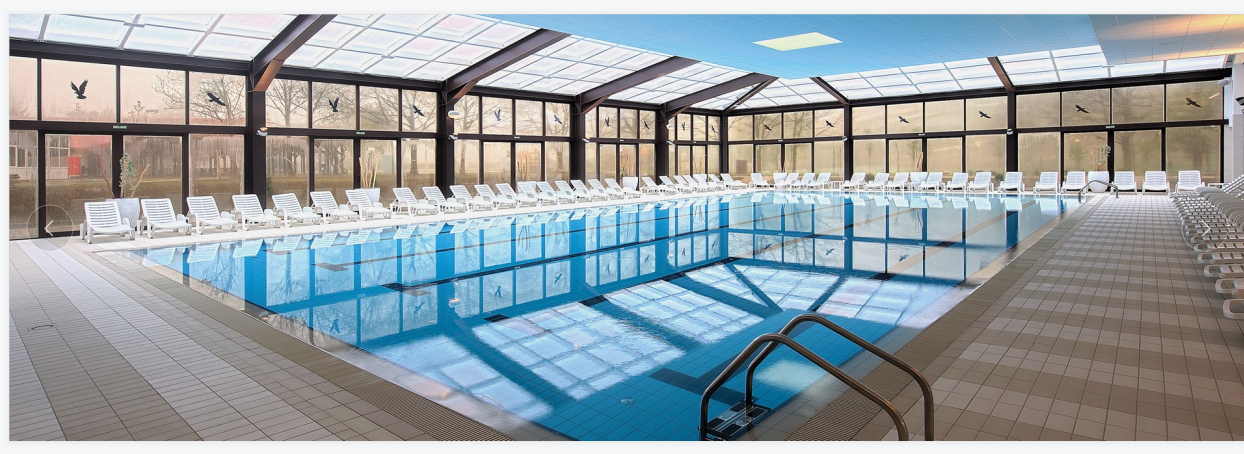
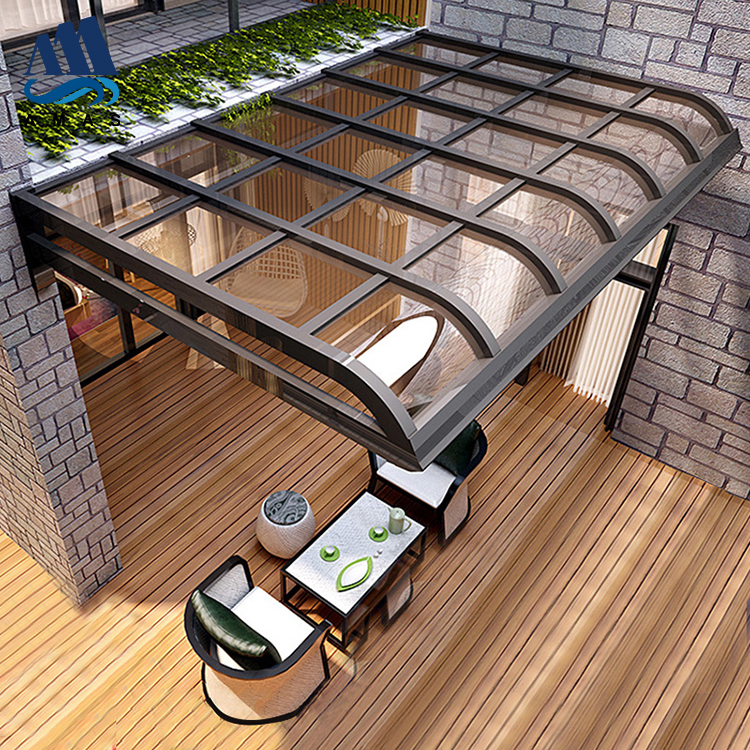
Building Material
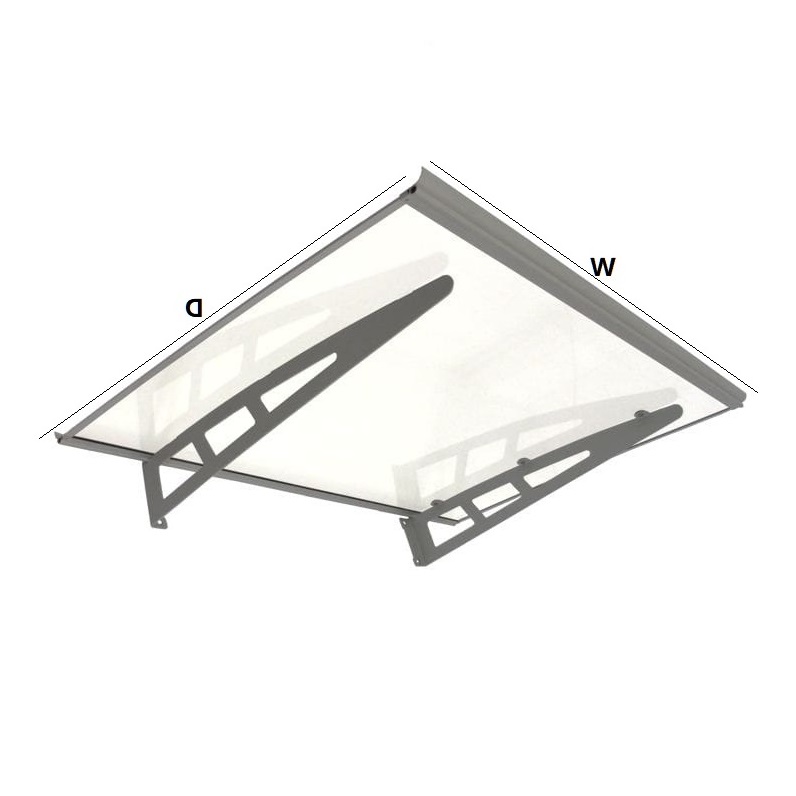
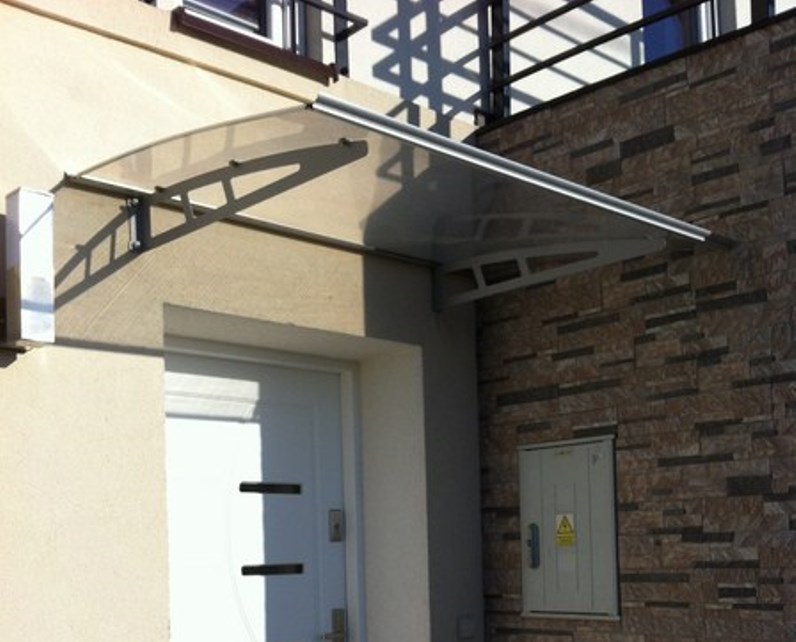
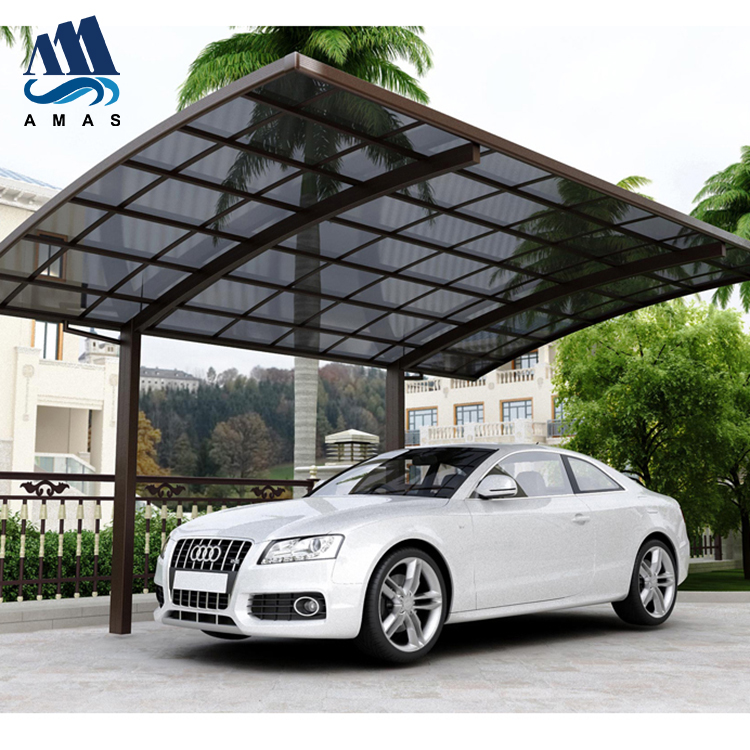
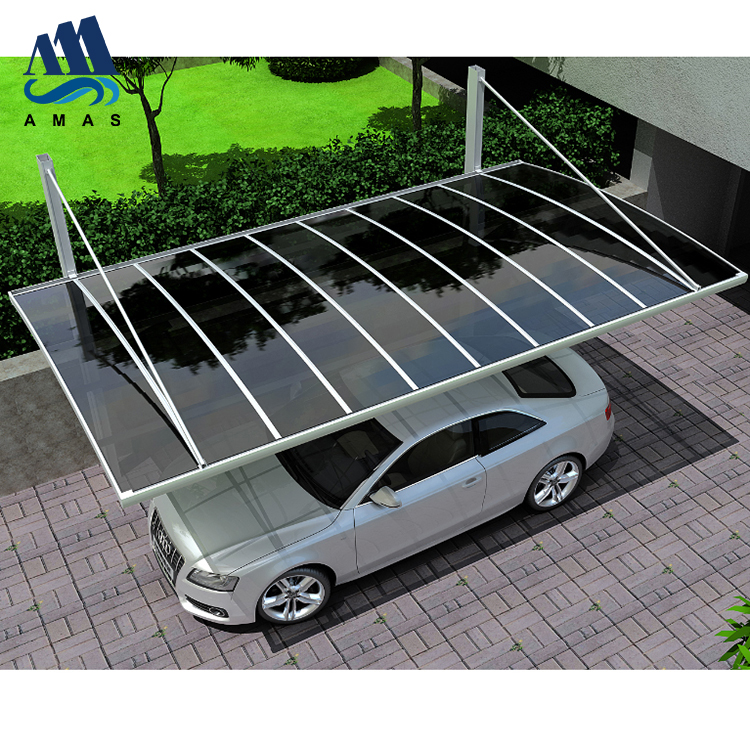
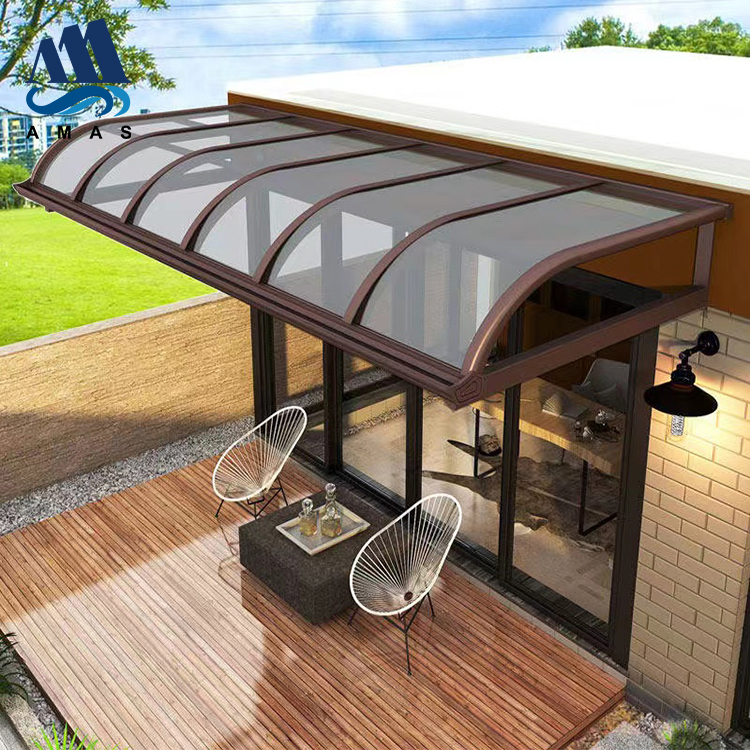
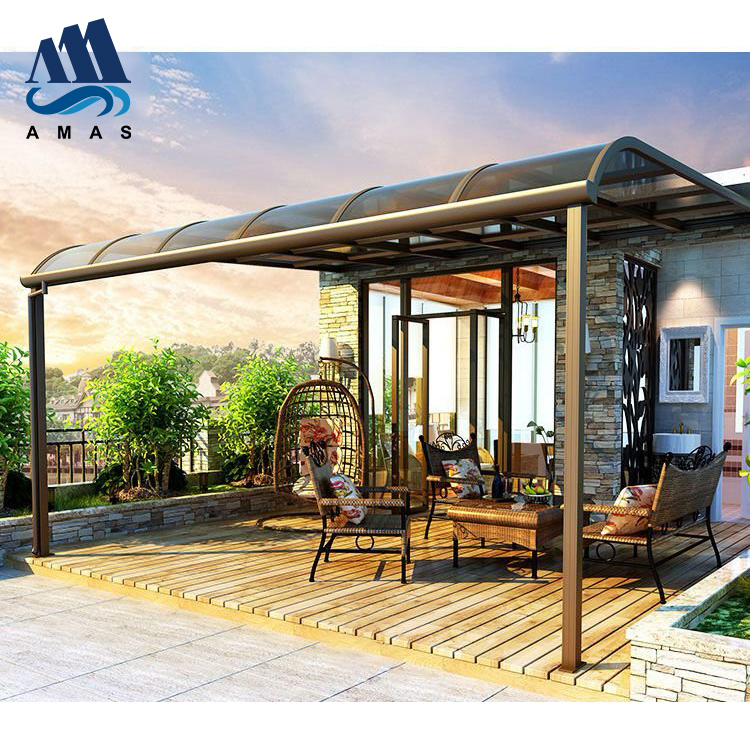
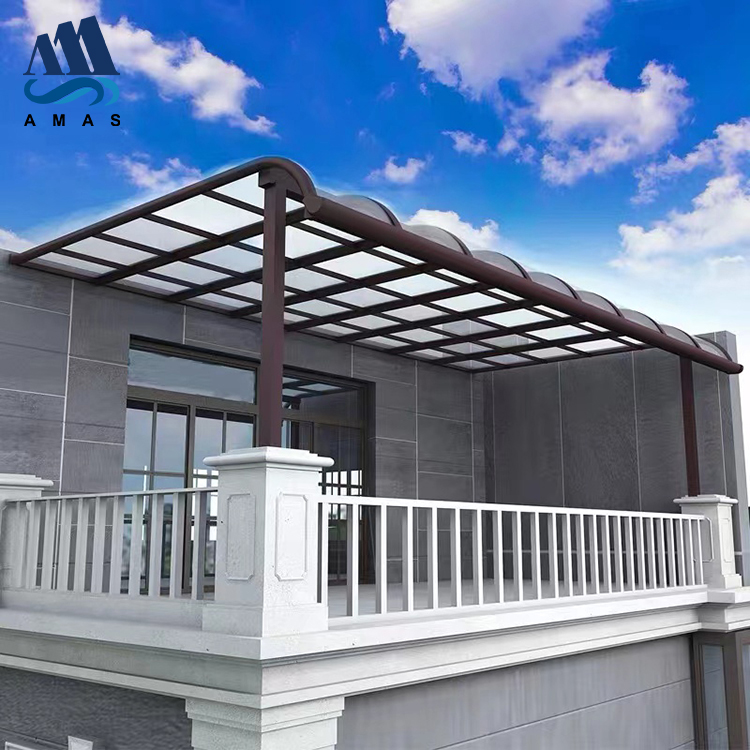
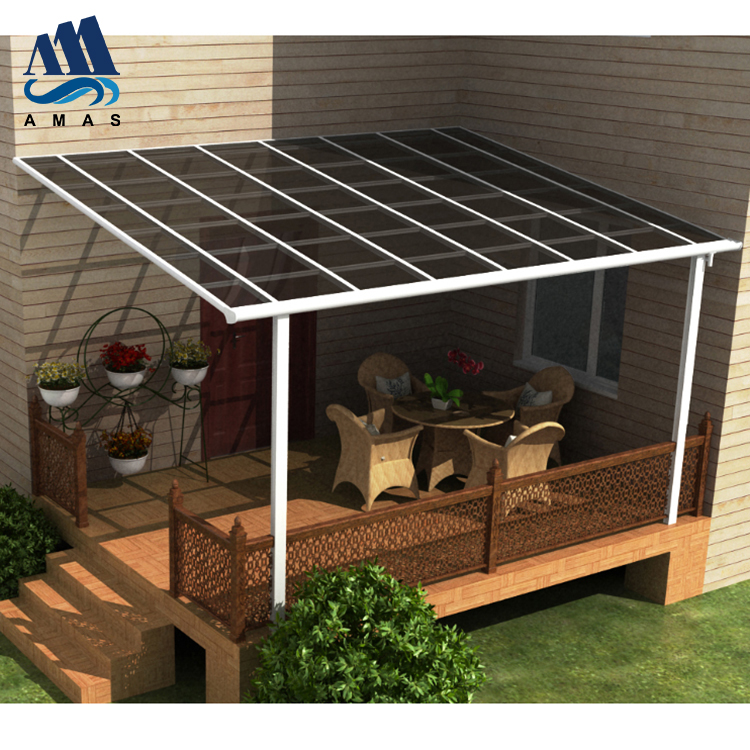
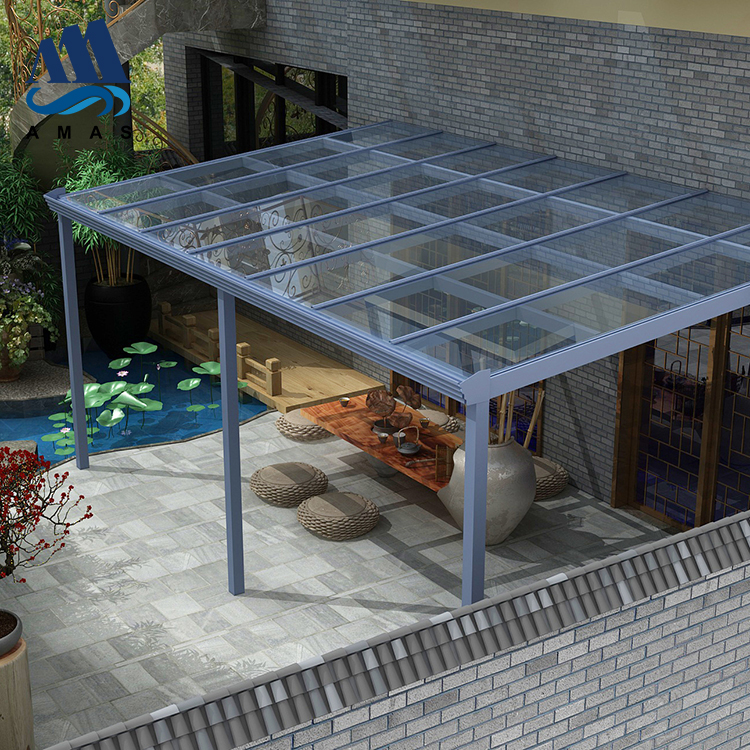
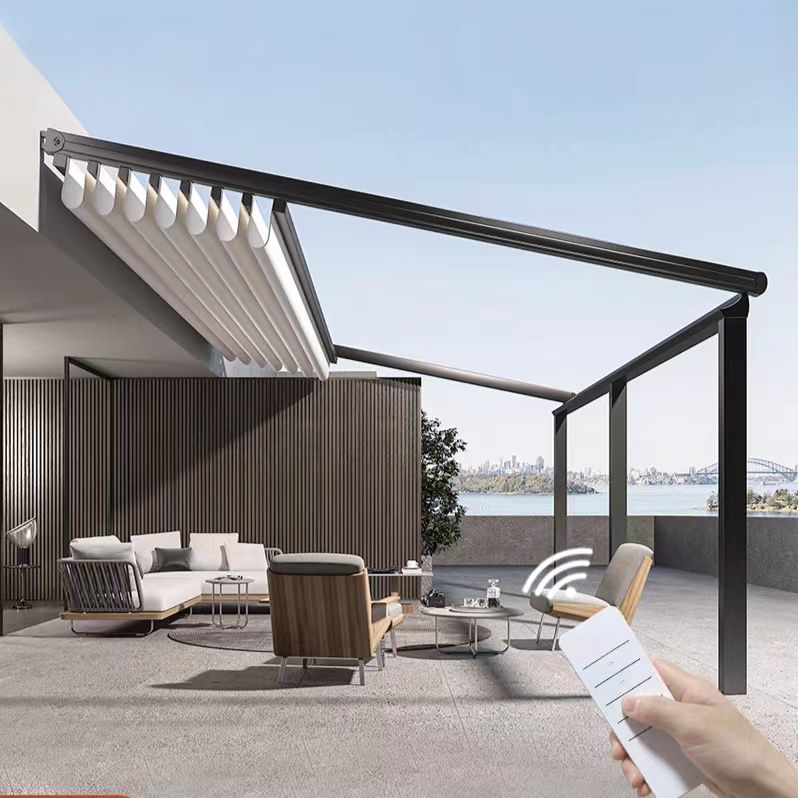
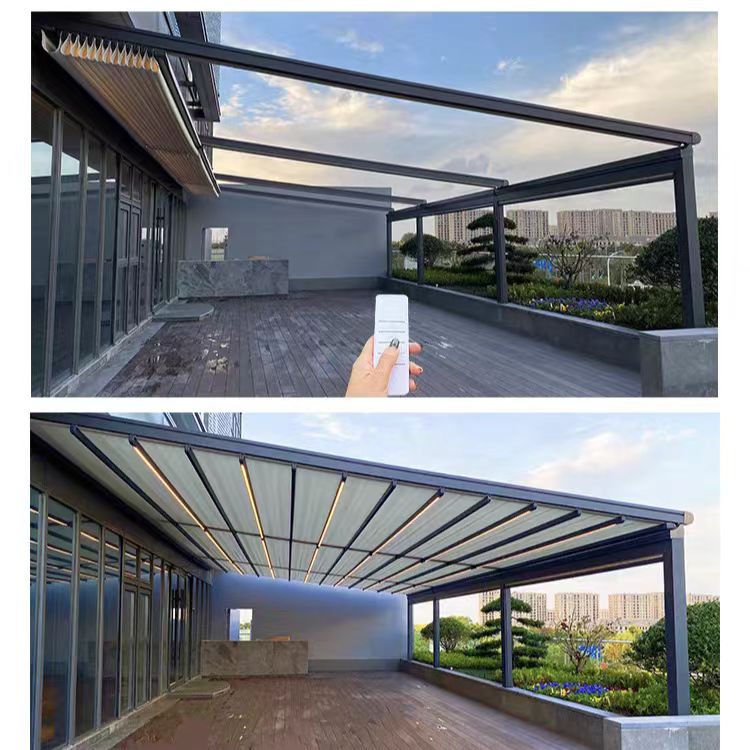
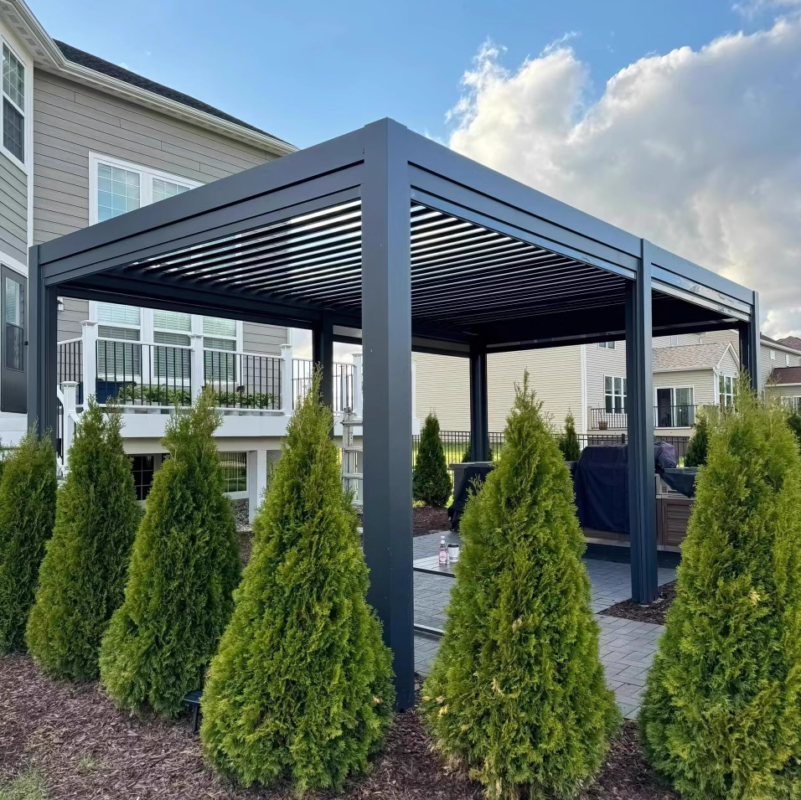
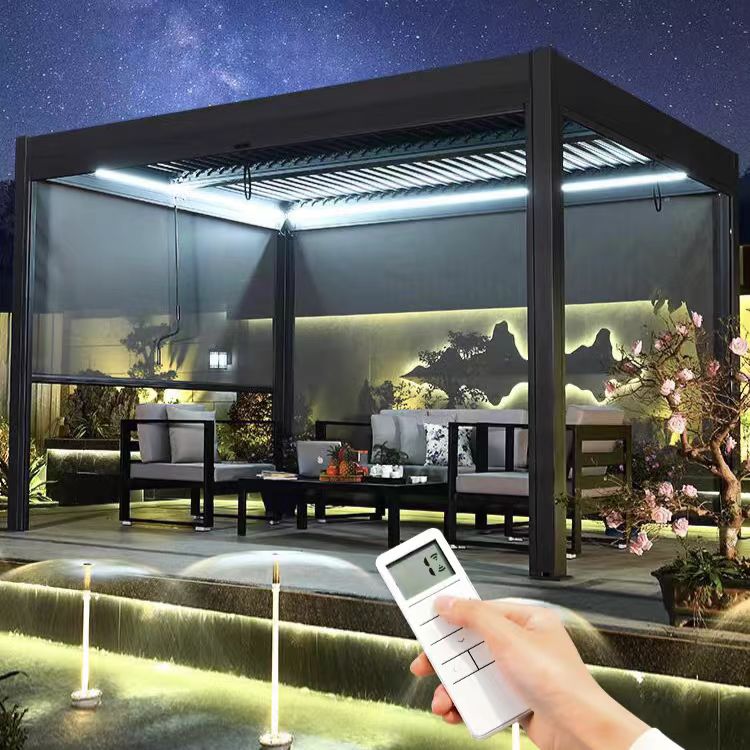
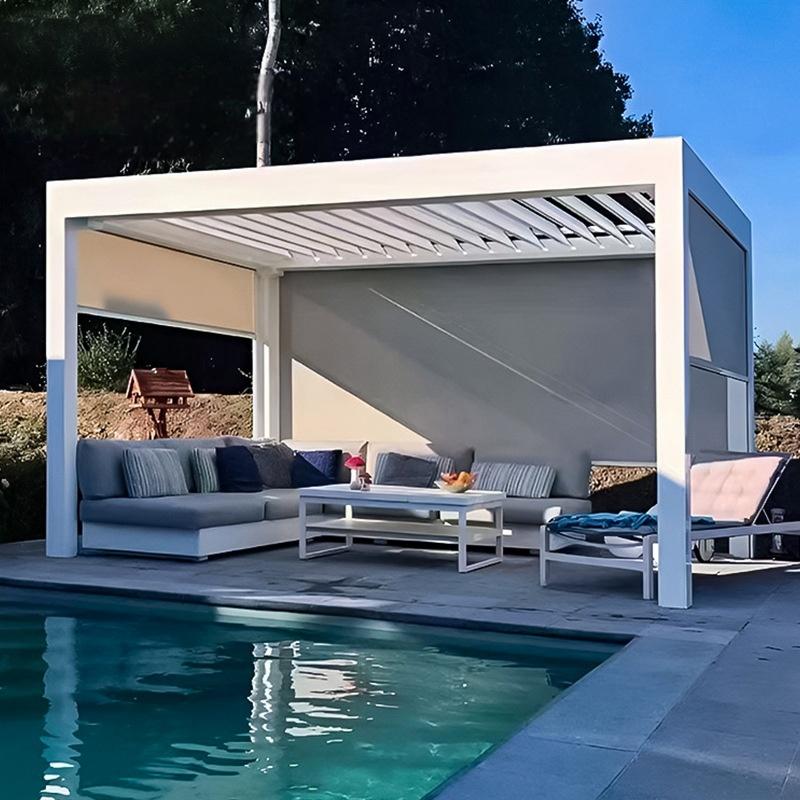
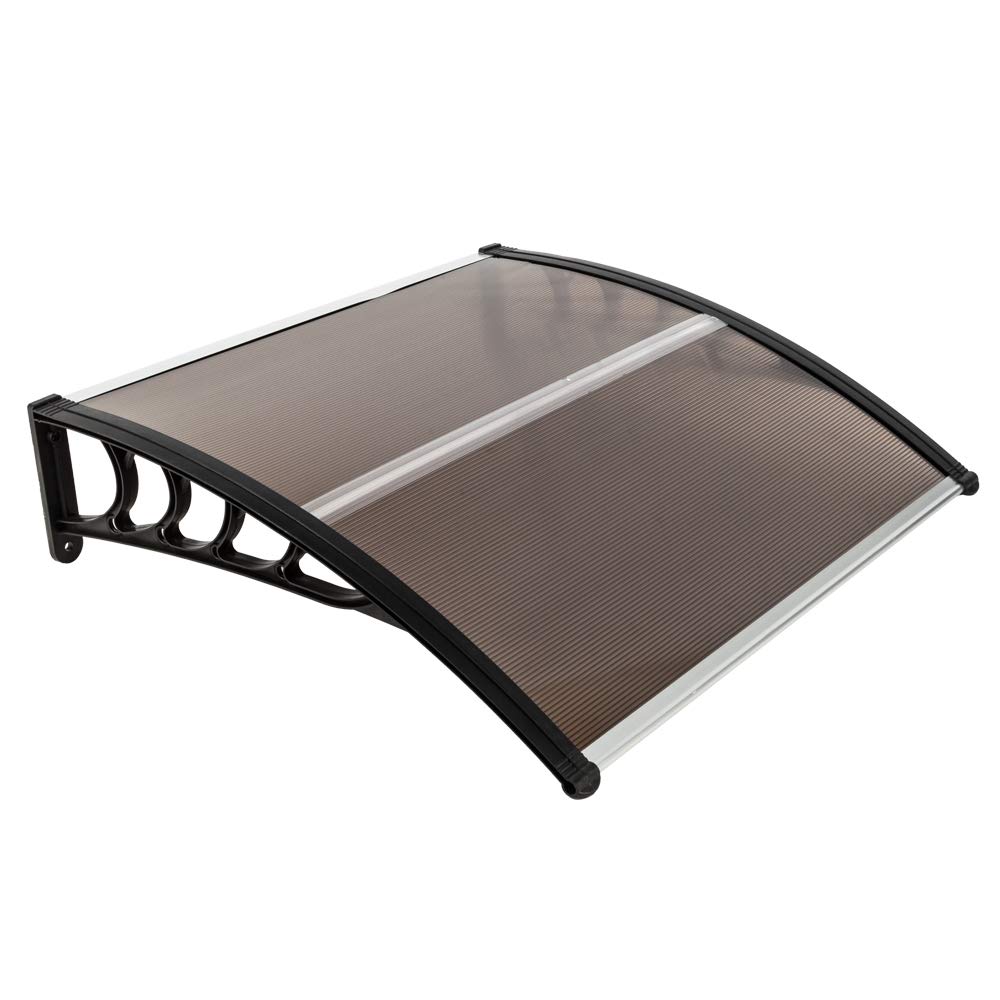
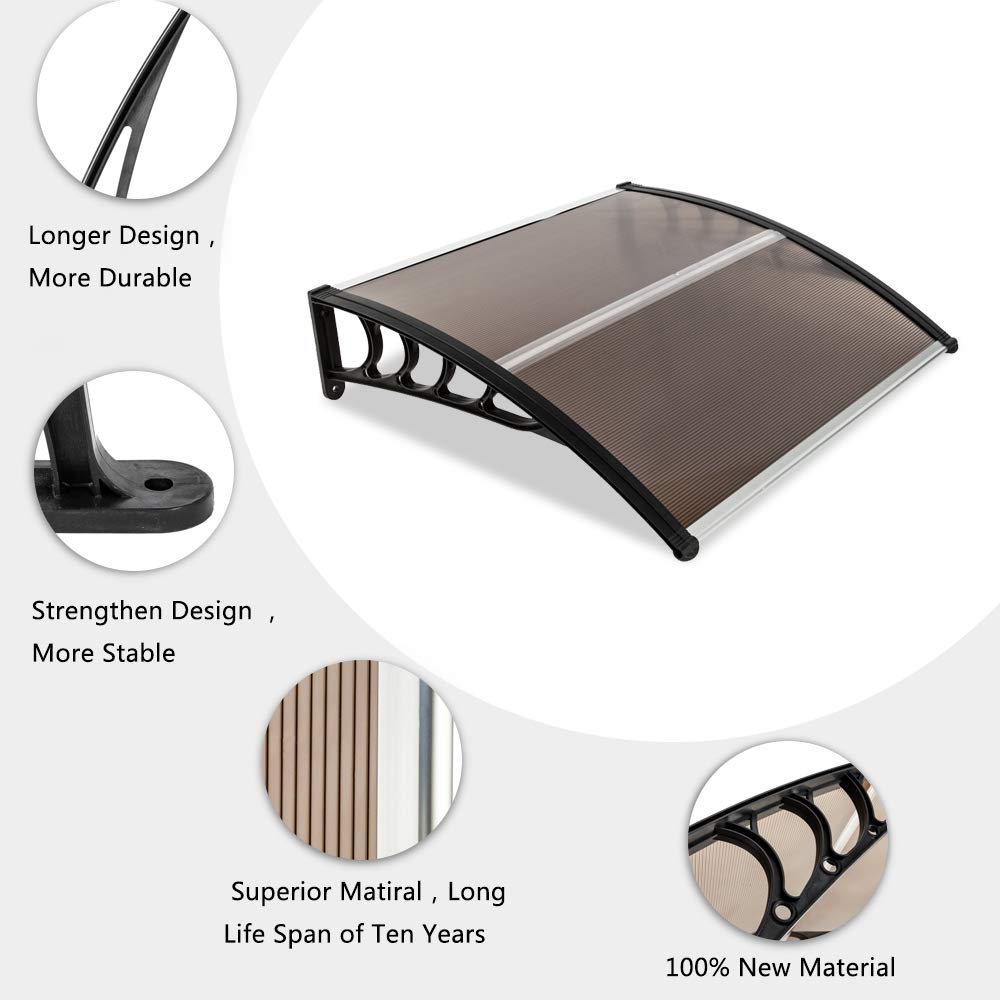
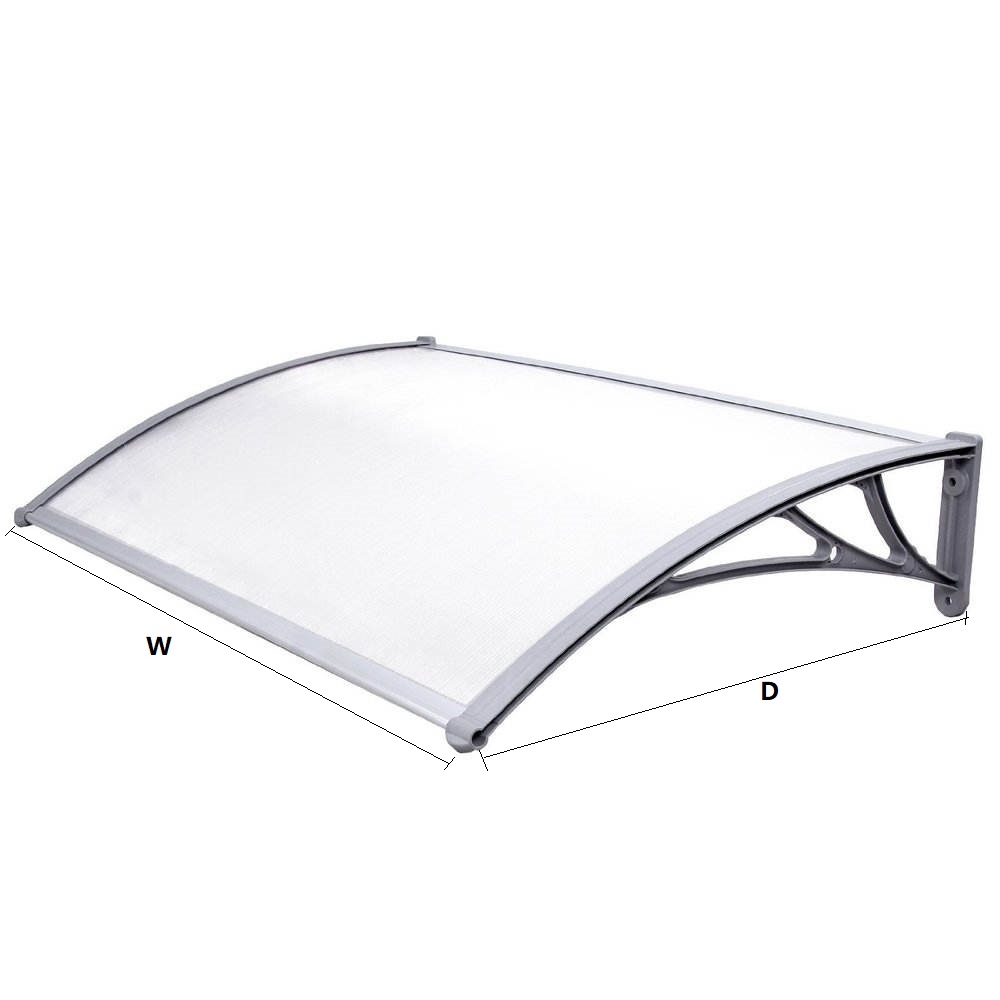
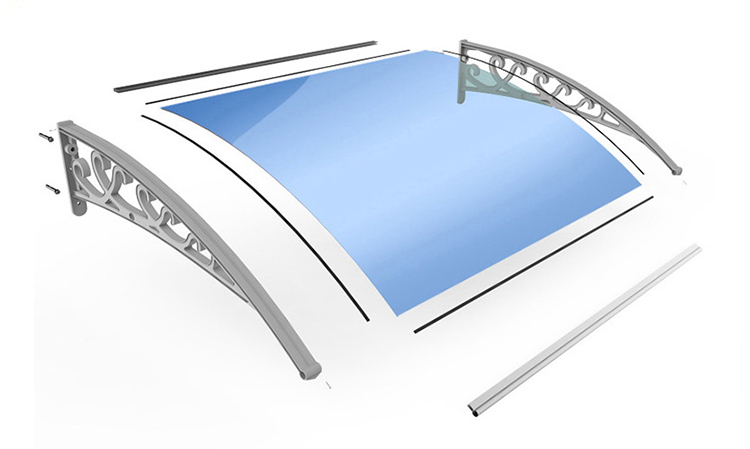
The second largest consumer of polycarbonate is the construction industry, such as for dome lamps, flat or curved glass, roof panels and acoustic walls. Polycarbonate is used to manufacture materials used in buildings. These materials need to be durable but lightweight.

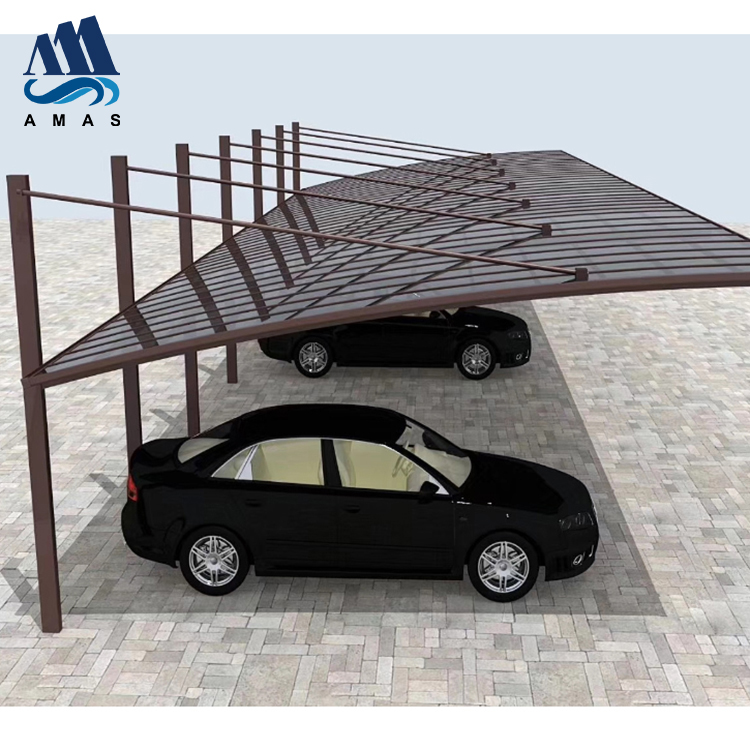
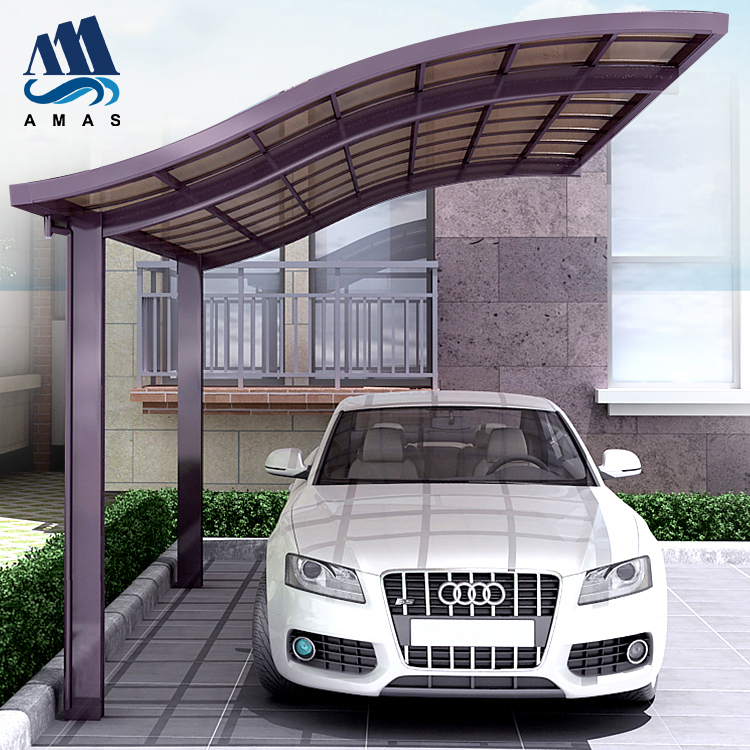
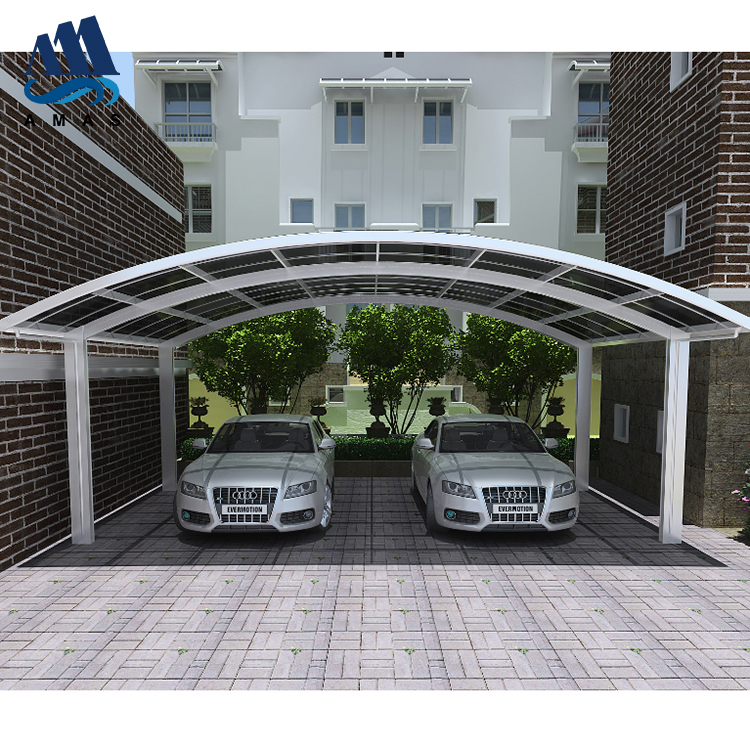
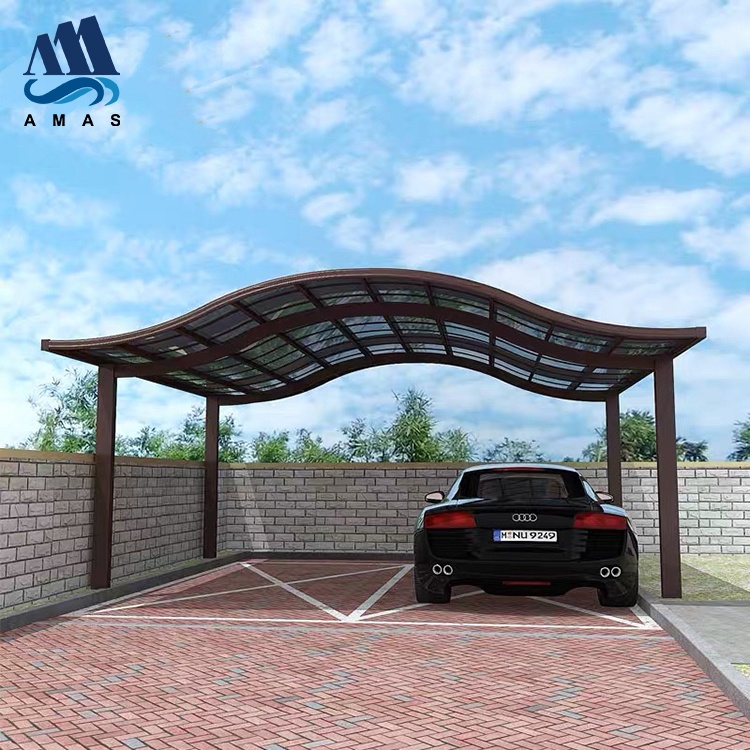
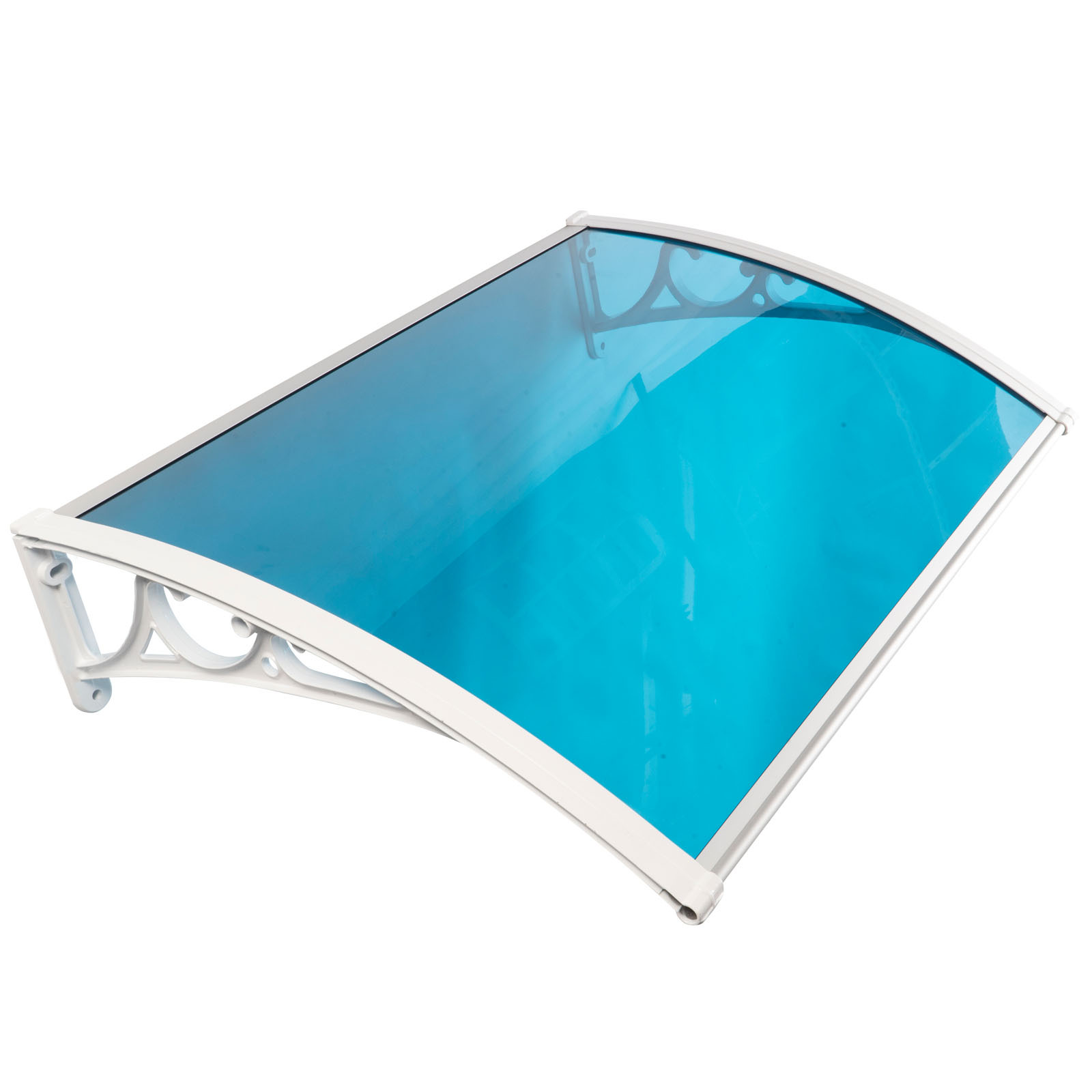
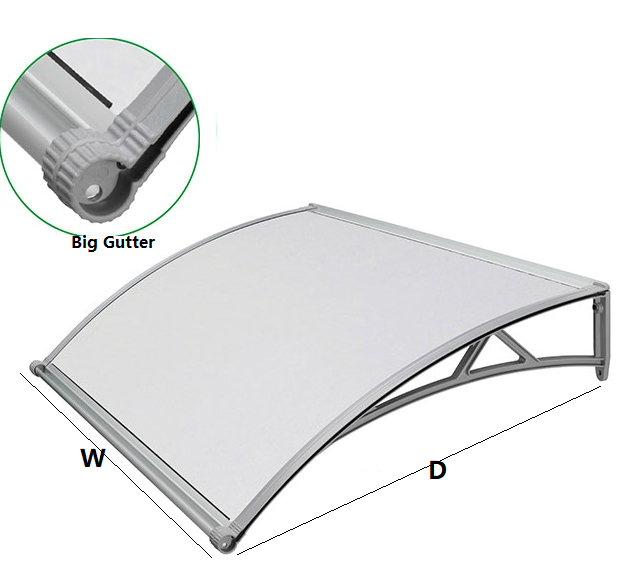
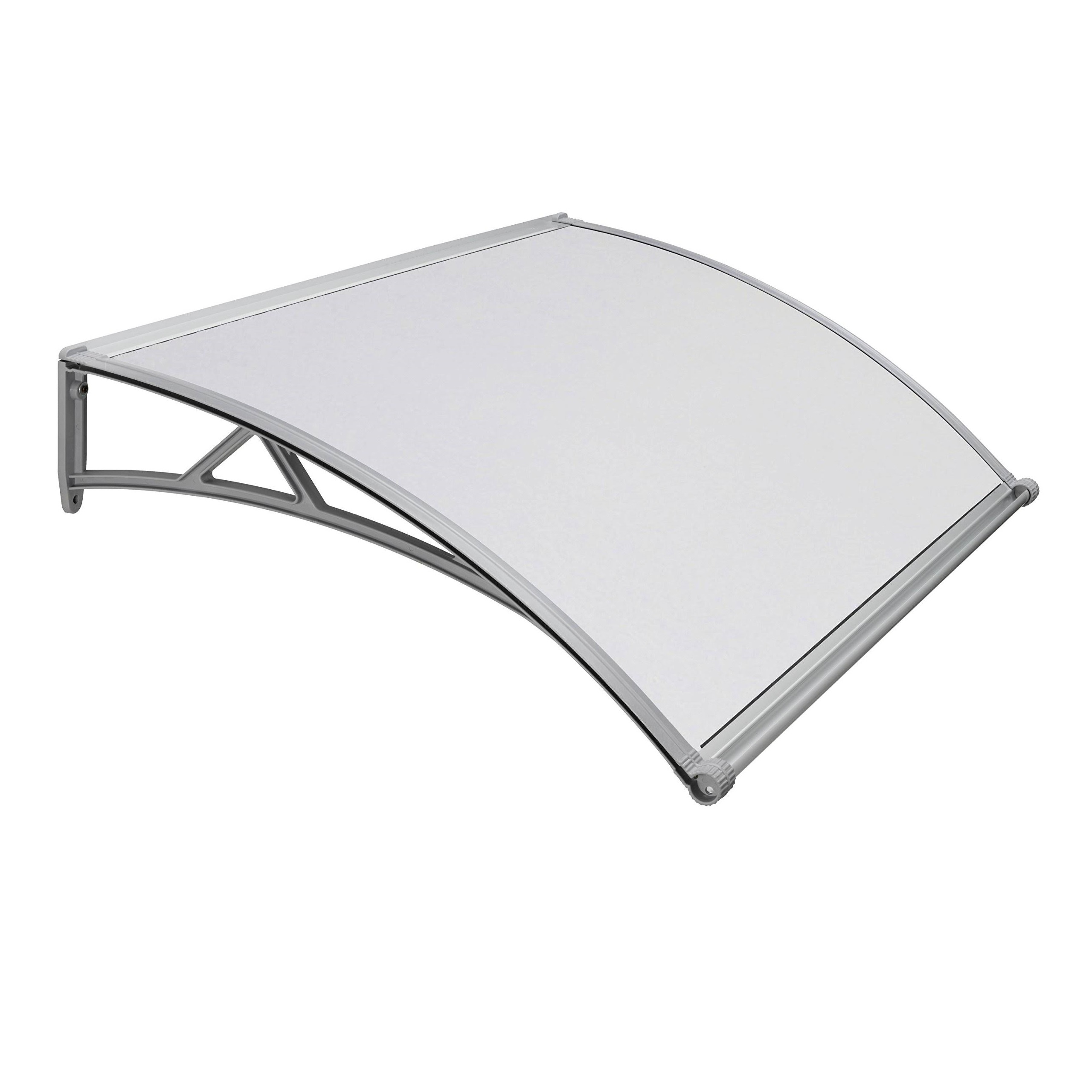
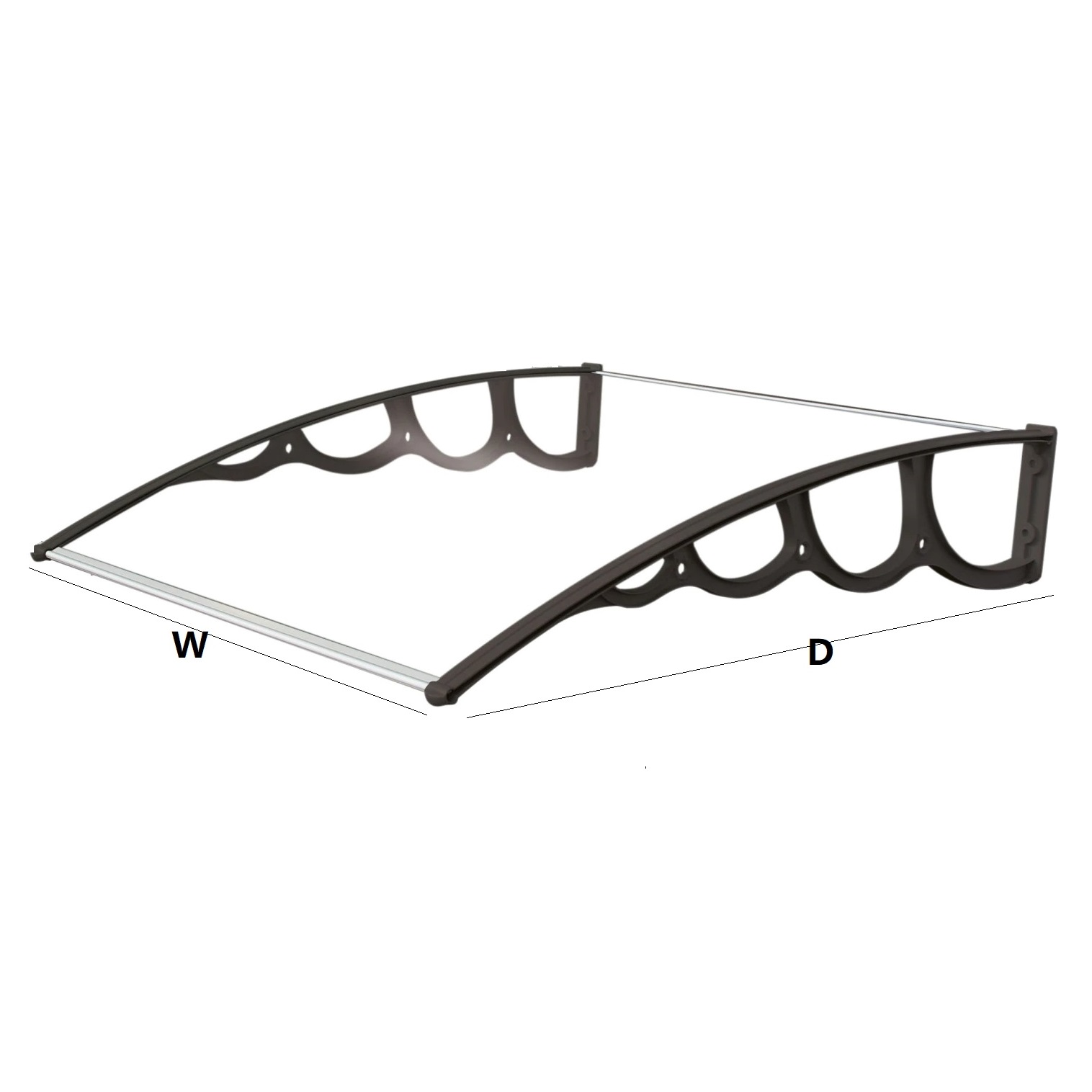
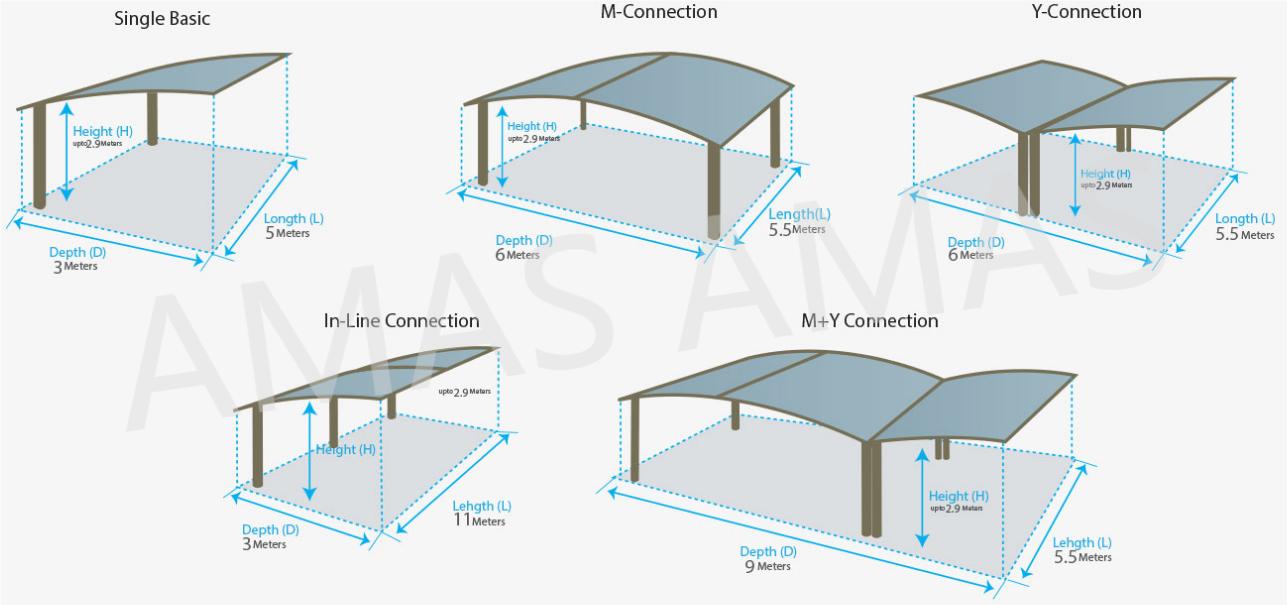
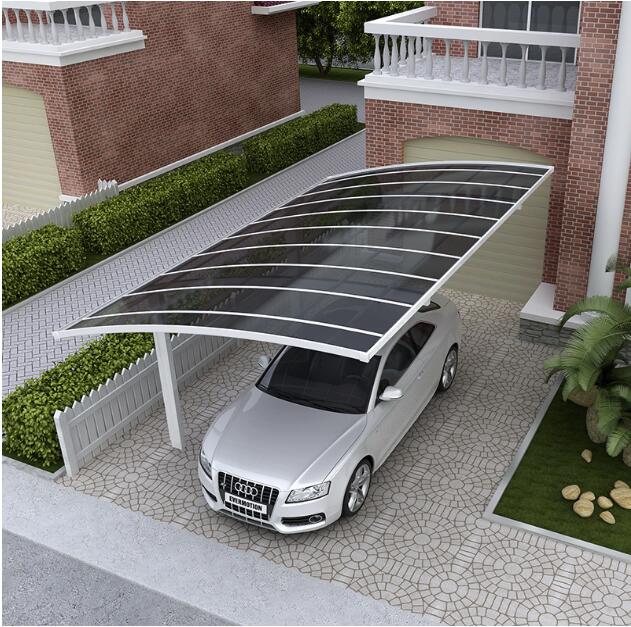
Amas Polycarbonate Carports AMS-CP-M1
3D Printing
Polycarbonate is widely used in 3DFDM printing and can produce plastic products with high melting point, durability and robustness. Compared with thermoplastic plastics such as polylactic acid (PLA) or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), polycarbonate is relatively difficult for amateurs to print, because it has a high melting point, is difficult to bond with the printing bed, is prone to warpage during printing, and is prone to moisture absorption in humid environments. Despite these problems, 3D printing using polycarbonate is common in professional communities.

Data Storage
The main polycarbonate market is the production of optical discs, DVDs and Blu-ray discs. These discs are produced by injecting polycarbonate into the mold cavity. There is a metal die on one side of the mold cavity, which contains the negative image of the disc data, while the other side is a mirror. Typical products for sheet/film production include advertising applications (logo, display, poster protection).












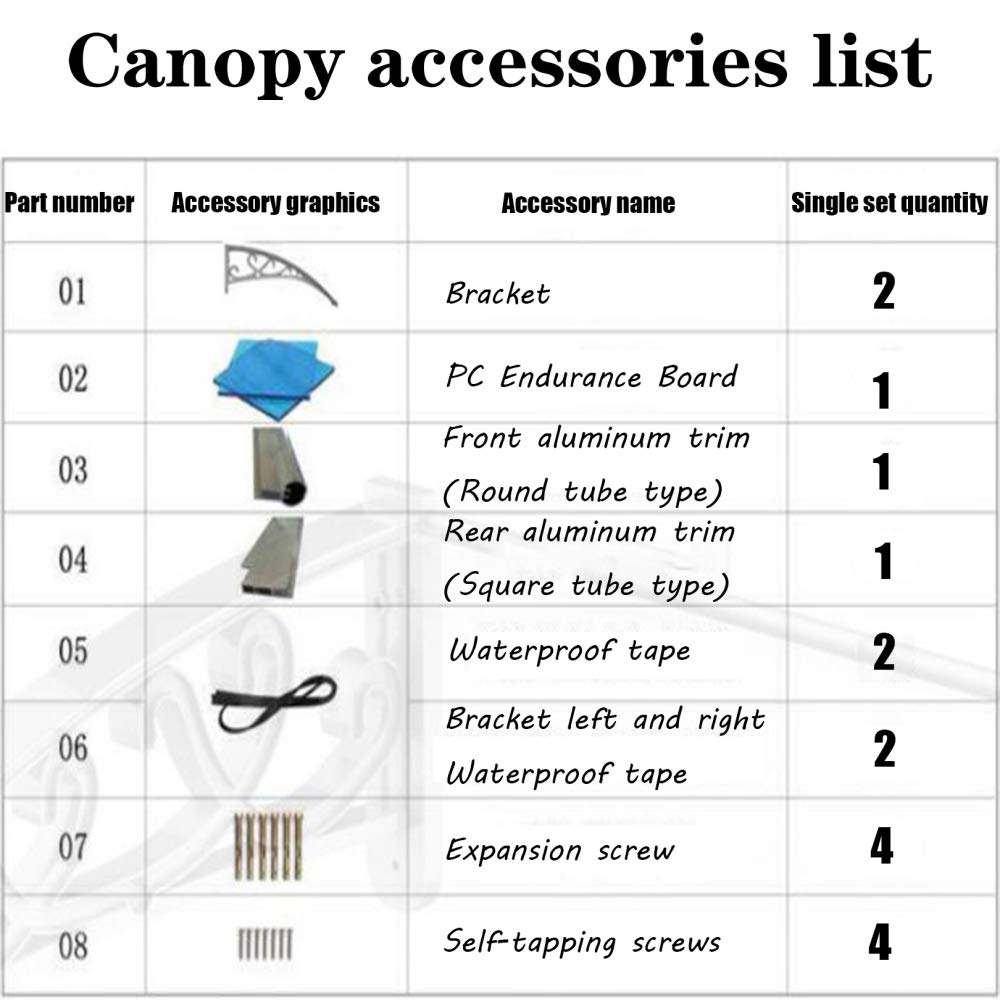
(整套).jpg)